Manufacturing, prototyping, and do-it-yourself projects have been transformed by 3D printing. Durability, strength, and performance depend on selecting the correct 3D print filament for functional pieces, though. Choosing the right filament guarantees dependability and lifespan whether you are printing industrial-grade prototypes, replacement parts, or mechanical components. This guide explores the best 3D printing filaments for functional parts, covering their properties, ideal use cases, and considerations for selecting the right material.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Filament for Functional Parts
1. Use Guidelines
Think about the use of your 3d-printed component. Nylon or polycarbonate might be suitable if great strength is needed. TPU is best for adaptability.
2. Problems Printing
Certain materials, including ABS and polycarbonate, require sealed chambers and precise temperature control. Two simpler but still reasonably strong substitutes are PLA+ and PETG.
3. Environmental Considerations
Choose PETG, Nylon, or ABS, which provide better resistance if the part comes into contact with chemicals, UV light, or humidity.
4. Financial Factors
Particularly costly are high-performance materials like polycarbonate and nylon. Among reasonably priced but robust choices are PETG and PLA+.
What Makes a Filament Suitable for Functional Parts?
When printing functional parts, the filament must possess key characteristics:
- Strength & Durability – Resistance to wear and mechanical stress.
- Heat Resistance – Ability to withstand high temperatures.
- Flexibility – Essential for shock-absorbing or bendable parts.
- Chemical & UV Resistance – Important for outdoor or industrial applications.
- Ease of Printing – Good layer adhesion and minimal warping.
Top Filaments for Functional Parts
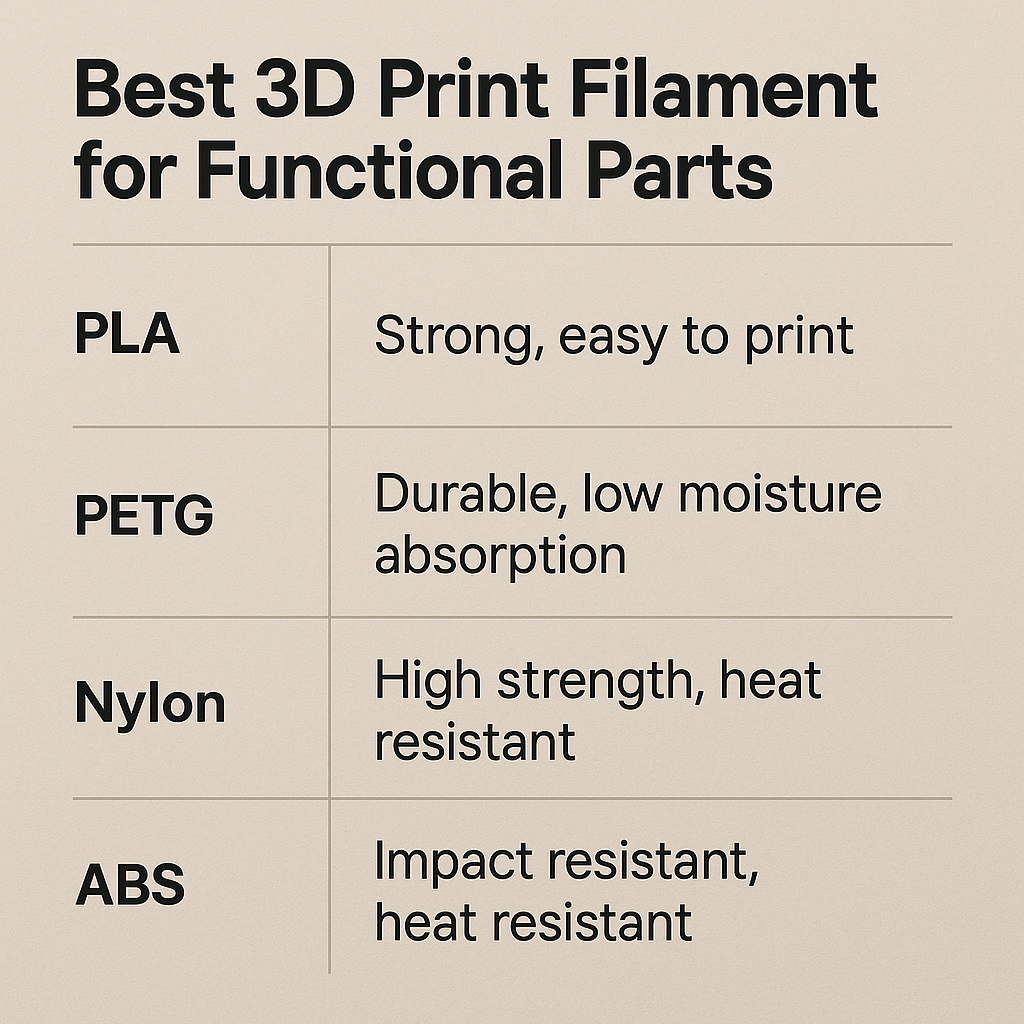
1. PLA+ (Polylactic Acid Plus)
]
Best for: General-purpose functional parts, prototypes, and household tools.
Pros:
- Easy to print, low warping.
- Higher strength than standard PLA.
- Biodegradable and eco-friendly.
Cons:
- Lower heat resistance (softens at ~60°C).
- Not ideal for high-stress mechanical parts.
2. PETG (Polyethene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified)
Best for: Durable consumer products, enclosures, and outdoor parts.
Pros:
- High impact resistance and flexibility.
- Excellent water and chemical resistance.
- Good balance of strength and ease of printing.
Cons:
- Prone to stringing if not properly tuned.
- Slightly lower rigidity than ABS.
3. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Best for: Heat-resistant and impact-resistant parts, as well as automotive components.
Pros:
- Stronger and more heat-resistant than PLA.
- Good toughness and machinability.
- Ideal for mechanical applications.
Cons:
- Requires a heated bed and enclosed chamber to prevent warping.
- Emits fumes; proper ventilation is necessary.
4. Nylon
Best for: High-strength functional parts, gears, and industrial applications.
Pros:
- Superior durability and wear resistance.
- High flexibility and low friction coefficient.
- Good resistance to impact and chemicals.
Cons:
- Absorbs moisture; needs proper storage.
- Requires high temperatures for printing.
5. Polycarbonate (PC)
Best for: Extreme strength applications, impact-resistant parts, and engineering projects.
Pros:
- High impact and heat resistance.
- Excellent mechanical strength and durability.
- Ideal for structural and industrial use.
Cons:
- Difficult to print; requires high temperatures and an enclosure.
- Prone to warping without proper bed adhesion.
6. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
Best for: Flexible, shock-absorbing, and wearable parts.
Pros:
- High flexibility and elasticity.
- Excellent vibration damping and abrasion resistance.
- Suitable for medical and sports applications.
Cons:
- Difficult to print at high speeds.
- Requires a direct-drive extruder for best results.
READ MORE – How to 3D Print a Filipino Parol Christmas Lantern
FAQs
1. What is the strongest filament for 3D printing?
Polycarbonate (PC) is one of the strongest filaments, offering high impact resistance and heat tolerance.
2. Is PETG better than ABS for functional parts?
PETG is easier to print and has better chemical resistance, while ABS is stronger and more heat-resistant. Choose based on your application.
3. Does filament storage affect performance?
Yes, materials like Nylon and TPU absorb moisture, which affects print quality. Store them in airtight containers with desiccants.
4. Can I use PLA for functional parts?
PLA+ is suitable for low-stress functional parts, but it lacks heat and impact resistance compared to ABS or Nylon.
5. What’s the best flexible filament for functional parts?
TPU is the best flexible filament, providing durability and shock absorption for wearable and vibration-dampening applications.
Conclusion
The strength, heat resistance, flexibility, and durability your application calls for will determine which 3D print filament is appropriate for functional parts. Unique advantages suited to various functional requirements abound from PLA+, PETG, ABS, Nylon, Polycarbonate, and TPU. Choosing the correct material will enable you to produce 3d-printed, long-lasting, highly performing parts.



